THE kinetic energy is the energy associated with velocity of a body. If there is speed, there will certainly be that kind of energy. For objects that are at rest, the kinetic energy is zero, as the velocity of such bodies is zero.
Determination of kinetic energy
kinetic energy is determined as a function of body mass in motion, which is measured in kilograms (kg), and the speed developed by it, which is determined in meters per second (m/s).
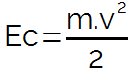
The unit of measure adopted by the International System of Units (SI) for kinetic energy it is joule (J). This unit is a tribute to the English physicist James Prescott Joule for their contributions to studies related to the heat and to energy. See correspondence between joule (J) and calorie (cal) units:
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
1 cal = 4.2 J
Relationship between kinetic energy and work
Work is the amount of energy expended in performing a certain activity and is defined broadly as the product of the force applied to an object and the displacement suffered by it.
When a force is applied in favor of an object's movement, there will be increased speed and consequent increase in kinetic energy, therefore, we can establish a relationship between energy kinetics and work. The call Kinetic Energy Theoremshows that the work done on an object is just equal to the change in kinetic energy suffered by it.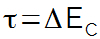
By Joab Silas
Graduated in Physics
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
JUNIOR, Joab Silas da Silva. "What is kinetic energy?"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/o-que-e/fisica/o-que-e-energia-cinetica.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.

