Questions about chemical balances in Enem are very recurrent. With this in mind, we created this material, which brings the most important themes about this branch of Physical Chemistry covered in the National High School Exam (Enem).
Among the issues related to chemical equilibrium, we have equilibrium constant in terms of concentration in mol/L and in terms of pressure, ionic equilibrium constant, ionization constant, equilibrium shift, pH and pOH, hydrolysis constant, buffer and constant of solubility.
Among the subjects described above, some of them gain greater prominence in Enem:
Balance shift
Ionization constant
pH
saline hydrolysis
Video lesson on Chemical Balance at Enem
1. Equilibrium shift in Enem
1.1- (Enem 2015) Hypoxia or altitude sickness consists of decreased oxygen (O2) in the arterial blood of the body. For this reason, many athletes experience discomfort (headaches, dizziness, shortness of breath) when practicing physical activity at high altitudes. Under these conditions, there will be a decrease in the concentration of oxygenated hemoglobin (HbO
2) in balance in the blood, according to the relationship: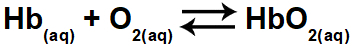
The change in the concentration of oxygenated hemoglobin in the blood occurs because of:
a) the elevation of blood pressure.
b) the increase in body temperature.
c) reducing the temperature of the environment.
d) the drop in oxygen partial pressure.
e) the decrease in the amount of red blood cells.
Oxygenated hemoglobin (HbO2) is found in the reactants (right side) of the equation. The exercise asks which of the options would lead to a change in oxygenated hemoglobin in the blood, that is, it would shift the balance to the left or to the right.
a) False. Increased blood flow has nothing to do with increased blood pressure.
b) False. The temperature does not change the balance provided.
c) False. The temperature does not change the balance provided.
d) True. Decreasing the partial pressure of oxygen reduces the amount of oxygenated hemoglobin, shifting the balance to the left.
e) False. The fall in the number of red blood cells will cause both the number of hemoglobins and oxygenated hemoglobins to fall.
1.2- (Enem 2011) Soft drinks have become more and more targets of public health policies. Glue products contain phosphoric acid, a substance that is harmful to the fixation of calcium, a mineral that is the main component of the tooth matrix. Caries is a dynamic process of imbalance in the process of dental demineralization, loss of minerals due to acidity. It is known that the main component of tooth enamel is a salt called hydroxyapatite. The soda, due to the presence of sucrose, decreases the pH of the biofilm (bacterial plaque), causing the demineralization of the dental enamel. Salivary defense mechanisms take 20 minutes to 30 minutes to normalize the pH level, remineralizing the tooth. The following chemical equation represents this process:

Considering that a person consumes soft drinks daily, a process of dental demineralization may occur as a result of the increased concentration of:
a) OH-, which reacts with Ca ions2+, shifting balance to the right.
b) H+, which reacts with the OH hydroxyls-, shifting balance to the right.
c) OH-, which reacts with Ca ions2+, shifting balance to the left.
d) H+, which reacts with the OH hydroxyls-, shifting balance to the left.
e) Ca2+, which reacts with the OH hydroxyls-, shifting balance to the left.
Right answer: Letter B
Resolution
The demineralization process shifts the balance to the right. When a person drinks soda, they are ingesting an acidic material, that is, increasing the amount of H+ in the middle. the H+ quickly interacts with the OH- of equilibrium, reducing the amount of OH-. In this way, the balance is shifted to the right, demineralizing the tooth.
1.3- (Enem-2013) One of the steps in water treatment is disinfection, with chlorination being the most used method. This method consists of dissolving chlorine gas in a solution under pressure and applying it to the water to be disinfected. The chemical reaction equations involved are:

The disinfecting action is controlled by hypochlorous acid, which has a disinfection potential about 80 times greater than the hypochlorite anion. The pH of the medium is important because it influences the extent to which hypochlorous acid ionizes. For the disinfection to be more effective, the pH of the water to be treated must be closer to:
a) 0
b) 5
c) 7
d) 9
e) 14
Right answer: Letter B
According to the text, the best disinfectant action is performed by the substance HClO. Therefore, every interpretation and conclusion must be directed towards a way to obtain this substance.
The substance HClO is present in the second balance, so an interesting tactic is to shift this balance to the left. For this, according to the principle of Le Chatelier, we have the option to increase the amount of H+ (adding an acidic substance, pH less than 7) or increase the amount of Cl-.
It is noteworthy that, in the first equation, there is another chemical equilibrium, which presents the HClO species-, which has an affinity with H+, shifting balance to the left. This is a move we don't want.
Therefore, we must use an acidic pH (below 7). However, this pH should not be too acidic to avoid a lot of H cations.+ in the middle.
See too:Chemical balance in caves
2. pH and saline hydrolysis in Enem
2.1- (Enem-2017) Several natural products can be obtained from plants through the extraction process. Lapachol is of the naphthoquinone class. Its structure has an enol hydroxyl (pKa = 6.0) that allows this compound to be isolated from the ipe sawdust by extraction with an adequate solution, followed by simple filtration. Consider that pKa = -log Ka and that Ka is the acid constant of the lapachol ionization reaction.

Which solution should be used to extract lapachol from ipê sawdust more efficiently?
a) Na solution2CO3 to form a lapachol salt.
b) Acetic acid/sodium acetate buffer solution (pH = 4.5).
c) NaCI solution in order to increase the ionic strength of the medium.
d) Na solution2ONLY4 to form an ion pair with lapachol.
e) HCI solution in order to extract it through an acid-base reaction.
The statement indicates that the pKa of the substance is 6.0. This pKa value must be used in the pKa expression:
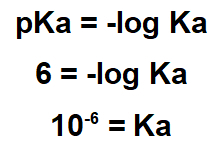
As your Ka is small, lapachol is an acidic substance, so to remove it, it is useful to use a basic substance.
a) True. Salt is basic, as it comes from a strong base (because it is from the IA family), and CO3 comes from a weak acid (H2CO3).
b) False. The buffer solution is acidic, and we need a base.
c) False. NaCl is a neutral salt, as it comes from a strong base (because it is from the IA family), and Cl comes from a strong acid (HCl).
d) False. At2ONLY4 is a neutral salt, as Na comes from a strong base (because it is from the IA family), and SO4 comes from a strong acid (H2ONLY4).
it's fake. HCl is an acid, and we need a base.
2.2- (Enem- 2014) Aiming to minimize environmental impacts, Brazilian legislation determines that chemical residues released directly into the receiving body have a pH between 5.0 and 9.0. An aqueous liquid waste generated in an industrial process has a hydroxyl ion concentration equal to 1.0.10-10 mol/L. To comply with the legislation, a chemist separated the following substances, available in the company's warehouse: CH3COOH, Na2SO4, CH3OH, K2CO3 and NH4Cl.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
In order for the residue to be released directly into the receiving body, which substance could be used to adjust the pH?
a) CH3COOH
b) In2ONLY4
c) CH3oh
d) K2CO3
e) NH4Cl
Right answer: Letter D
Resolution
Step 1: Determine the pH of the residue.
The exercise indicates that the residue has a hydroxide concentration equal to 10-10.
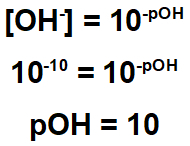
Therefore, we can calculate the pH of this residue:

From the above, we have that the residue has an acidic character, as its pH is less than 7. Thus, to neutralize it, it is essential to use a substance with a basic character.
Step 2: Determine the character of each salt to indicate which one is basic, as the CH3COOH (alternative a) is an acid, and CH3OH (alternative c) is an alcohol, organic class with acidic character.
b) Neutral salt, as the Na comes from a strong base (because it is from the IA family), and the SO4 comes from a strong acid (H2ONLY4).
d) Basic salt, as K comes from a strong base (because it is from the IA family), and CO3 comes from a weak acid (H2CO3).
e) Acid salt, as NH4 comes from a weak base (NH4OH), and Cl comes from a strong acid (HCl).
2.3- (Enem- 2014) A researcher notices that the label on one of the jars in which he keeps a concentrate of digestive enzymes is illegible. He doesn't know which enzyme the glass contains, but suspects it's a gastric protease, which works in the stomach by digesting protein. Knowing that digestion in the stomach is acidic and the intestine is basic, he assembles five test tubes with food different, add the enzyme concentrate to solutions with a determined pH and wait to see if the enzyme acts in any their. The test tube in which the enzyme must act to indicate that the researcher's hypothesis is correct is the one that contains:
a) potato cube in solution with pH = 9.
b) piece of meat in solution with pH = 5.
c) boiled egg white in solution with pH = 9.
d) portion of noodles in solution with pH = 5.
e) butter ball in solution with pH = 9.
Right answer: Letter B
The exercise requires from the student good interpretation and correlation with biochemical knowledge of foods. He informs that the researcher thinks the enzyme is digestive, acts at an acidic pH and acts on proteins (because it is a protease).
If this enzyme acts in an acidic environment, the pH must be less than 7. Meat is made up of proteins, while pasta is made up of carbohydrates. So the right answer is alternative b.
2.4- (Enem- 2012) A housewife accidentally dropped water from the defrosting of a fish in the refrigerator, which left a strong and unpleasant smell inside the appliance. It is known that the characteristic odor of fish is due to amines, and that these compounds behave as bases. In the table, the hydrogen concentrations of some materials found in the kitchen are listed, which the housewife is thinking of using when cleaning the refrigerator.

Among the materials listed, which ones are appropriate to alleviate this odor?
a) Alcohol or soap
b) Lemon juice or alcohol
c) Lemon juice or vinegar
d) Lemon juice, milk or soap
e) Soap or soda/soda ash
Right answer: Letter C
Resolution
The exercise proposes a problem situation in which a housewife's refrigerator has a strong odor caused by a substance of a basic nature. Thus, it is questioned which materials would be interesting to solve this problem.
To neutralize a base, it is necessary to use a material of an acidic nature or with a pH lower than 7. How exercise provided the values of H concentrations+ of the materials, it was enough to use each one in the expression below:

Thus:
Juice: pH = 2
Milk: pH = 6
Vinegar: pH = 3
Alcohol: pH = 8
Soap: pH = 12
Barrel: pH = 12
Materials with an acidic character are juice, vinegar and milk. Thus, only alternative c brings materials of an acidic nature.
3. Equilibrium constant in Enem
3.1- (Enem-2016) After their complete wear, the tires can be burned for power generation. Among the gases generated in the complete combustion of vulcanized rubber, some are pollutants and cause acid rain. To prevent them from escaping into the atmosphere, these gases can be bubbled into an aqueous solution containing a suitable substance. Consider the substance information listed in the table below:

Among the substances listed in the table, the one capable of most efficiently removing polluting gases is (a)
a) phenol.
b) pyridine.
c) methylamine.
d) potassium hydrogen phosphate.
e) potassium hydrogen sulfate.
Right answer: Letter D
Resolution
The exercise poses a problem situation in which polluting gases promote acid rain. Then, he asks which of the substances mentioned would be interesting to neutralize these gases and, consequently, avoid acid rain.
To avoid acid rain, acid gases must be neutralized using a basic solution. Substances with this characteristic are those that preferentially release OH groups- in the middle. In the table, pyridine, methylamine and potassium hydrogen phosphate are basic substances.
Thus, in order to determine the substance capable of removing pollutant gases more efficiently, we must analyze the value of the ionization constant. The greater the constant, the greater the ability to release OH-. So, the potassium hydrogen phosphate it is the most suitable substance in this case.
3.2- (Enem-2015) Several acids are used in industries that dispose of their effluents in water bodies, such as rivers and lakes, which can affect the environmental balance. To neutralize the acidity, calcium carbonate salt can be added to the effluent in appropriate amounts, as it produces bicarbonate, which neutralizes the water. The equations involved in the process are presented:

Based on the values of the equilibrium constants of reactions II, III and IV, at 25O C, what is the numerical value of the equilibrium constant of reaction I?
a) 4.5x10-26
b) 5x10-5
c) 0.8x10-9
d) 0.2x105
e) 2.2x1026
Right answer: Letter B
Resolution
This exercise involves constant ionization. Initially, it is essential to understand that equation I is actually the result (sum) of equations II, III and IV. Therefore, to initiate the resolution, we must use the principles of Hess's law.
Step 1: Use of Hess' Law.
Inverting equation II and keeping equations III and IV, we have:
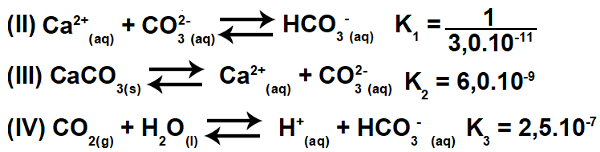
Thus, we can observe that the anion CO3-2 and the H cation+ will be eliminated, and the sum of the equations will result in equation I.
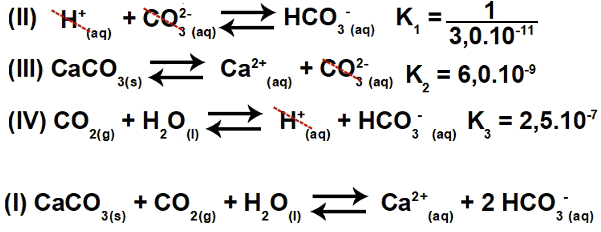
Step 2: constant calculation
The equilibrium constant of the ionization equation is always given by multiplying the constants of the other equations:

By Me. Diogo Dias



