In the text "Title or Mass Percentage” we saw how to calculate the relationship between the mass of the solute and the mass of the solution, for solid, liquid and gaseous solutions. In this text, however, we will see that it is also possible to calculate the titer in terms of volume, for solutions with liquid or gaseous components.

The title in volume can be calculated by the expression:
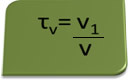
Consider as an example an aqueous solution of ethyl alcohol used as an antiseptic and disinfectant, which was prepared by adding 70 mL of pure alcohol to enough water to make up to a volume of 100 mL of solution. So we have:
τ = 70 ml = 0,7
100ml
We can express the title in percentage too, just multiplying the result by 100%. So in this case we have a 70% ethyl alcohol solution, which means that out of every 100 volume units of the solution, 70 volume units are alcohol.
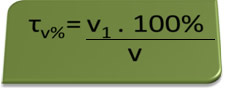
In the case below, we have a 70% ethyl alcohol solution in a 250 mL volume of solution; which means that 175 mL are alcohol, according to the calculations:
100 mL 70 mL alcohol
250 mL x
x = 70. 250
100
X = 175 mL of alcohol

However, we cannot say that in this case we have 75 mL (250-175) of water. Unlike mass titre, in which we can add the mass of the solvent to the mass of the solute to find the mass of the solution, this cannot be done in relation to the volume titer.

Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
This means that the solution volume is not equal to the sum of the solvent volume and the solute volume (although often the difference can be considered negligible). This is because the intermolecular forces that exist in these liquids influence the final volume.
In the case of the aforementioned solution, of ethyl alcohol, for example, when we mix alcohol with water, there is a contraction of the total volume of the solution; that is, the final volume will be smaller than if we added the volume of alcohol and water alone. This is because the alcohol molecules establish bonds or hydrogen bonds with the water molecules, reducing the spaces between them.
Therefore, in this and other cases, the volume of the solution must be measured experimentally when not provided in the exercise.
The percentage by volume is widely used in cases of alcoholic beverages and commercial alcohol, as mentioned above. See two important applications of this calculation:
- Breathalyzer: the breathalyzer measures the concentration of ethyl alcohol in the blood, and in Brazil it is forbidden for anyone to drive any type of vehicle with a blood alcohol content equal to or above 0.1% in volume. A person with this alcohol content has, for each liter of blood, 1 mL of alcohol, as shown by the following calculations:
τv%=V1. 100%
v
0,1 % = V1. 100%
1L
V1 = 0,1% → V1 = 0.001 L = 1 mL
100%

- Ethanol content in gasoline: in Brazil, gasoline is regulated by the addition of ethanol. But the ethanol content in gasoline must be at most 24% by volume of anhydrous alcohol (since gasoline must be water-free). The more ethanol is added to gasoline, the more the fuel's color becomes lighter and its density increases.
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Volume Title of a Chemical Solution"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/titulo-volume-uma-solucao-quimica.htm. Accessed on June 28, 2021.
Chemistry

How the Breathalyzer works, alcohol concentration, breathalyzer, reactions involving ethyl alcohol, types of breathalyzers, potassium dichromate, fuel cell, catalyst, electron release, acetic acid, hydrogen, conce


