THE mucormycosis, also called zygomycosis or “black fungus”, is a disease caused by fungi of the order Mucorals. It is considered a infection opportunistic, since it usually affects patients with immunological problems. It is rarely triggered in immunocompetent patients. It is noteworthy that mucormycosis is a non-communicable disease, and contamination by the fungus occurs, in most cases, through inhalation of spores.
Treatment involves the use of antifungal agents and surgeries to remove the area affected by the fungus. An increase in the number of cases of mucormycosis and in association with cases of Covid-19. Experts believe that the onset of the disease in patients with covid-19 may be related to the drugs used to treat this disease, which reduce the immunity in the individual.
Read more: Immune system - ensures our body's protection
What is mucormycosis?
Amucormycosis is a opportunistic infection, potentially fatal, caused by fungi belonging to the order Mucorals, being the most frequent gender the
Rhizopus.This infection is serious and usually affects people who have a weakened immune system. Some of the patients most affected by the disease are those in chemotherapy, under corticosteroid therapy, organ transplants solids, with diabetic ketoacidosis or diabetes poorly controlled, or who suffered major burns.Transmission of mucormycosis
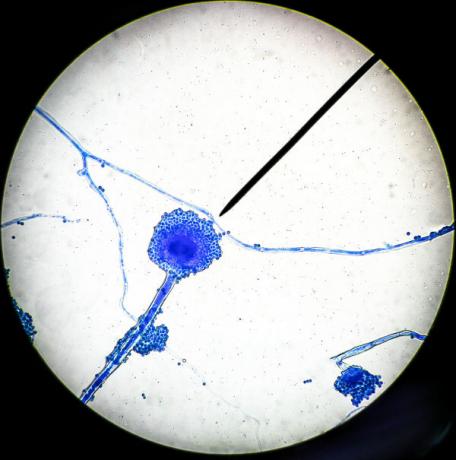
Mucormycosis is mainly acquired by inhalation, through the inhalation of spores produced by the fungus that causes it. The fungi that cause mucormycosis can be found in different places, such as in the soil, in plants, in vegetables in decomposition, and in animal manure. Less often, mucormycosis can be contracted by contact of spores with skin wounds. Mucormycosis is a non-communicable disease.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
Clinical manifestations of mucormycosis
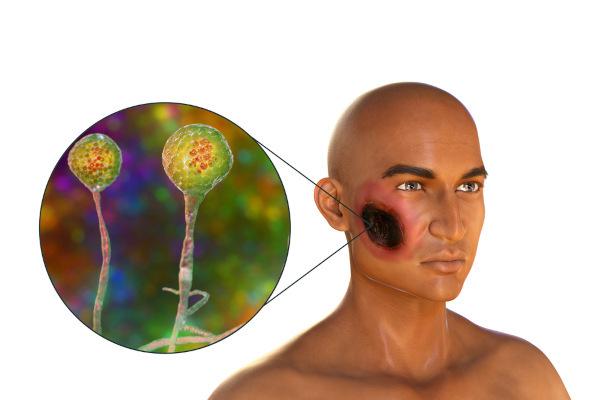
The clinical manifestations of mucormycosis can vary and may occur rhinocerebral, cutaneous, pulmonary, gastrointestinal involvement and disseminated. Rhinocerebral involvement is the most frequent one.
This infection usually starts in the paranasal sinuses and causes swelling of the face and periorbital (around the eyes). The disease rapidly progresses to necrosis gives skin and from the palate, pain in the eyes, upper eyelid droop, eyeball protrusion, facial paralysis, dilated pupil even after light stimulation (paralytic mydriasis), deep coma and death. The mortality rate is approximately 50% in this situation.
The second place most affected by mucormycosis is the lung, a condition known as pulmonary mucormycosis. The clinical manifestations of this condition include fever, cough, difficulty breathing, chest pain, sputum production and sputum blood from the tracheobronchial tree or lung parenchyma.
Diagnosis and treatment of mucormycosis
The diagnosis of mucormycosis is based on the analysis of the patient's clinical manifestations in association with the performance of biopsies, histopathological examination and imaging tests. As mucormycosis is a fungal disease, treatment includes the use of antifungals. In some situations, it is necessary to perform surgeries aimed at removing the parts of the body affected by the fungus.
Mucormycosis and covid-19
Mucormycosis was highlighted during the pandemic of covid-19 due to increased cases of the disease in May 2021 in India. At the time, it was reported that many of the individuals infected with the fungus were patients with covid-19 or had recently recovered from the disease.
The relationship between covid-19 and the development of mucormycosis can be explained, according to experts, by the fact that drugs used in the treatment of covid-19 they can increase the fragility of our immune system, making the individual more susceptible to opportunistic diseases.
It is important to highlight that it is believed that the high number of patients with mucormycosis in India is due to the fact that the country has one of the highest rates of diabetes in adults in the world, and this disease is a risk factor for development gives disease fungal.
By Vanessa Sardinha dos Santos
Biology teacher

