O skeletal system it's composed by bones and cartilage which are perfectly arranged in the formation of our skeleton. The adult human skeleton is formed by 206 bones, which act to support the body, protect vital organs, guarantee movement, production of blood cells and storage of some mineral salts, such as calcium and phosphorus.
The bones
Bones are made up of a special type of connective tissue, O bone tissue, which has a mineralized intracellular matrix. This tissue, despite what many people think, is made up of living cells: osteoblasts, osteoclasts and osteocytes.
The first group of cells is responsible for the synthesis of bone matrix, these cells being related to bone repair. Osteoclasts act in the resorption of bone tissue. Osteocytes, on the other hand, are related to the maintenance of the matrix and its reabsorption when stimulated by parathyroid hormone.

→ bone classification
Didactically, it is customary to classify bones, according to their shape, into five main types: long, short, flat, irregular and sesamoid. Note below the main characteristics of each type:
long bones: have greater length in relation to width and thickness. Among its examples are the femur and the ulna.
short bones: all dimensions (length, width and thickness) are equivalent. Among its examples are the tarsus and the carpus.
Flat or laminar bones: they have thin thickness and equivalent length and width. As an example, we can mention the bones of the skull.
Irregular bones: it does not have a definite geometric shape. As an example, we can mention the vertebrae.
sesamoid bones: they are small and rounded, their main example being the patella.
These different types of bones are connected to each other through bone joints, which can be furniture, like the ones on the knee, or fixed (not allowing movement), such as those of the skull bones.
Read too:Spinal Care
the joints
At jointscan be defined as the location of unity in between two or more bones. Some joints allow the movement of our skeleton, and it is essential to emphasize that not all of them perform this function.
Joints can be classified, according to their degree of movement, into three basic types:
Synarthrosis: also called immobile joints.
Amphiarthrosis: characterized by being slightly mobile.
Diaarthrosis: capable of allowing great movement.
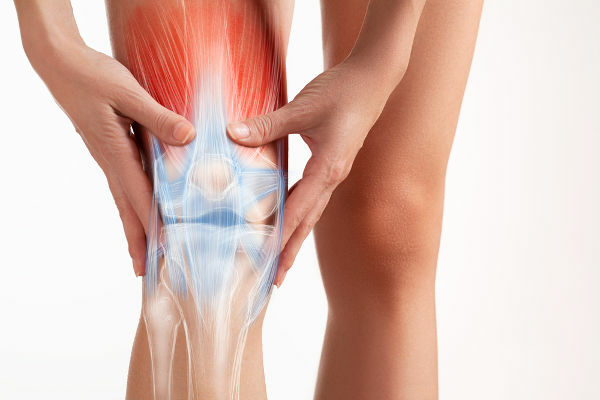
Joints can also be classified, according to the material found between the bones, into:
Fibrous joints: presence of fibrous connective tissue between bones. These joints have reduced mobility or are immobile. There are two types of fibrous joints: sutures and syndesmosis. At sutures they are found in the bones of the skull, and the connective tissue membrane observed between these is very thin. At syndesmosiss have characteristics similar to sutures but are not seen in the skull.
Cartilaginous joints: presence of cartilaginous tissue between bones and reduced mobility. We can classify these joints into synchondrosis, formed by hyaline cartilage, and in symphysis, that have fibrous cartilage. An example of a cartilaginous joint is the one between the pubic portions of the hip bones.
Synovial joints: presence of a capsule that delimits a joint cavity. In this cavity is found a viscous liquid that is called synovial fluid, which is rich in hyaluronic acid. This acid has an important lubricating effect. This type of joint can be seen in the complex knee joint.
Know more: What is rheumatosis arthritis and how to treat it?
Axial and appendicular skeleton
The human skeleton can be divided into two parts: axial and appendicular.
in the call axial skeleton,we have the skull, vertebrae, ribs, sternum and hyoid bone:
Skull: formed by 28 bones, it is the portion responsible for ensuring, mainly, the protection of the brain.
Vertebrae: they form the so-called vertebral column, which is made up of 26 bones (33 vertebrae). The spine guarantees the protection of the spinal cord.
Ribs: they form, in their 12 pairs, the rib cage. The top seven pairs are named real ribs and articulate directly with the sternum. The three sequential pairs articulate indirectly and are called false ribs. It is worth noting that the eleventh and twelfth rib are called the floating and do not articulate with the sternum.
Sternum: located in the anterior part of the chest.
Hyoid bone: it has no articulation and is found between the mandible and the larynx.
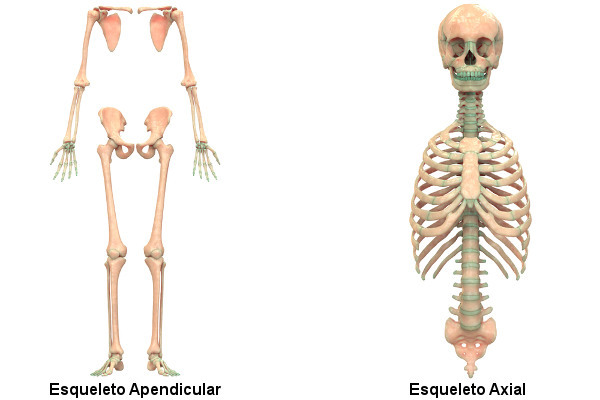
O appendicular skeleton, in turn, is formed by the limbs and the scapular and pelvic girdles.
Members: The upper limbs are formed by the humerus, which forms the arm, the ulna and radius, which form the forearm. The wrist and hands are formed, respectively, by the carpus and pasterns. The fingers, in turn, are formed by the phalanges. The lower limbs are formed by the femur, which is the thigh bone, by the tibia and fibula, which form the shin. The knee is made up of the patella and in the feet we find the tarsal, metatarsal and phalanges bones.
Scapular and pelvic girdles: The shoulder girdle, which is formed by the collarbone and scapula, joins the chest to the upper limbs, while the pelvic girdle, which is formed by the hip bone, connects to the sacrum and limbs. later.
Read too: Human Skeleton: Bone Names, Divisions and Functions
By Ma. Vanessa dos Santos
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/biologia/sistema-esqueletico.htm
