Electrolysis is a process widely used by the chemical industry, as it allows to obtain substances that do not exist free in nature, such as chlorine, iodine, caustic soda, among others.
Electrolysis is the opposite of the cell, in which electricity is obtained through redox reactions, that is, chemical energy is transformed into electrical energy. Already in electrolysis, electricity is used to produce redox reactions and chemical energy.
Hence the origin of its name, being that electro means "electric current" and lysis means "break". That's exactly what happens, the electrical current breaks or decomposes the substance being subjected to it.
The battery is a spontaneous process, electrolysis, however, it's a non-spontaneous process, which needs to be started by means of electrical current.
There are two types of electrolysis: a fiery and the in aqueous medium. In this text, we will deal with the first case.
The difference between igneous electrolysis and electrolysis in an aqueous medium is the form in which the substance that will be subjected to an electric current is.
In the case of igneous electrolysis, the ionic substance is in a liquid state, that is, molten, without the presence of water. The word "fiery" comes from the Latin fiery, which means “burning, inflamed”.In electrolysis, a container is used which is called a Cuba or electrolytic cell, where two electrodes are fitted through which the electric current will pass. Electrodes can be inert (do not change during electrolysis) or active (They suffer some kind of change during electrolysis). The most used are the inerts made of platinum or graphite.
Do not stop now... There's more after the advertising ;)
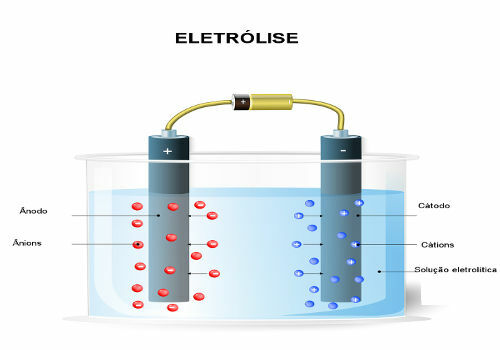
The electrodes are then connected to a direct current source (cell or battery). The negative pole of the battery will supply electrons to one of the electrodes, becoming negatively charged and will attract the cations (positive ions) from the molten substance. Because it attracts cations, this negative electrode is called a cathode. In it, cations receive electrons and reduce.
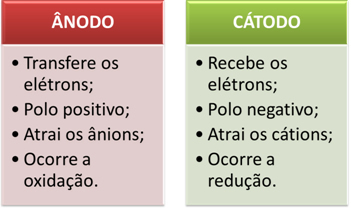
The positive electrode attracts anions (negative ions) and, due to this, it is called an anode. Anions discharge their electrons at the anode, undergoing oxidation.
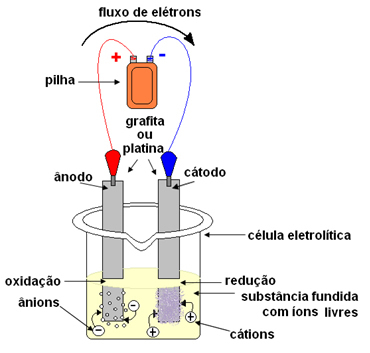
In batteries, the positive electrode is called the cathode and the negative one is the anode. Here in electrolysis it is the opposite, the anode is the positive pole and the cathode is the negative pole. However, in both cases, in the battery and in electrolysis, in the anode there is oxidation and in the cathode there is reduction.
Briefly, we have:
Another important fact is that the cell or battery used to generate the electric current must have a ddp (potential difference) equal to or greater than the reaction potential difference.
To better understand how the process of electrolysis takes place and how it breaks down substances producing important elements or simple substances, read the text Igneous Sodium Chloride Electrolysis.
By Jennifer Fogaça
Graduated in Chemistry
Would you like to reference this text in a school or academic work? Look:
FOGAÇA, Jennifer Rocha Vargas. "Igneous Electrolysis"; Brazil School. Available in: https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/eletrolise-Ignea.htm. Accessed on June 27, 2021.
d) Electrolysis is a spontaneous redox reaction.
Chemistry

Applications of Electrolysis, electroplating, nickel plating, chrome plating, nickel, chromium, cathode, sodium, aluminum, chlorine, caustic soda, hydrogen gas, igneous electrolysis, aqueous electrolysis, alkali metals, alkaline earth, gas chlorine.
Chemistry
Electrolysis, electrolyte solutions, electric current, oxidation-reduction reactions, spontaneous chemical process, chemical process non-spontaneous, transformer, artificial transformation, industries, alkali metals, alkaline earth, hydrogen gas, gas cl


