The capacity that the connections have to attract electrical charges is defined as Polarity, which takes on a different character depending on the connection where it is present.
Regarding the ionic and covalent bond, the latter makes the molecule non-polar. The molecule where the ionic bond is responsible for keeping atoms together has polarity.
The predominant bond between organic compounds is covalent, so they mostly become nonpolar compounds. The long carbon chains present in organic substances do not allow them any other character than non-polarity.
The explanation comes from the fact that the connection occurs between equal elements (Ç-Ç), therefore they have the same electronegativity scale. See an example:

non-polar molecule
The butane represented by the structure above is a gas, note that the bonding atoms are the same (4 carbons bonded together).
But it does not mean that every organic compound is non-polar, the presence of other atoms between carbons gives the molecule a polar character. Check out the example:
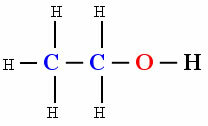
polar molecule
The presence of hydroxyl oh (Oxygen linked to hydrogen) caused the molecule of the organic compound Ethanol to show polarity.
Butane is used as a gas for lighters and Ethanol is the so-called common alcohol.
By Líria Alves
Graduated in Chemistry
Brazil School Team
See more!
Properties of organic compounds
Polarity – Find out why electronegativity influences the polarity of a call.
Polarity of ionic and covalent bonds
Organic chemistry - Chemistry - Brazil School
Source: Brazil School - https://brasilescola.uol.com.br/quimica/polaridade-dos-compostos-organicos.htm


