Organic Chemistry is a wide area of Chemistry that studies carbon compounds.
The knowledge of Organic Chemistry is approached in several ways and, thinking about it, we have put together proposed exercises, entrance exams and Enem questions for you to test your knowledge.
Also use the resolutions comments to learn even more about the subject.
Proposed exercises
question 1
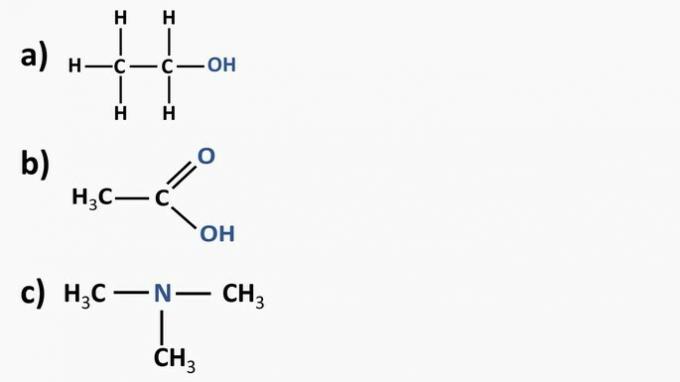
Look at the organic compounds below and identify the organic functions according to the highlighted functional groups. After that, name the substances.
Reply:
a) Organic compound: ethanol
- organic function: alcohol
- General formula: R—OH
- Identification: hydroxyl (OH) linked to the carbon chain
b) Organic compound: ethanoic acid.
- Organic function: carboxylic acid
- General formula: R—COOH
- Identification: carboxylic radical (COOH) linked to the carbon chain
c) Organic compound: trimethylamine
- Organic function: amine (tertiary)
- General formula:
- Identification: nitrogen linked to three carbon chains
question 2
In organic chemistry, compounds are recognized by the chains formed by carbon and hydrogen. However, other elements can be part of the chemical structure of these compounds, such as oxygen.
Select the alternative where the two organic compounds have oxygenated organic functions.
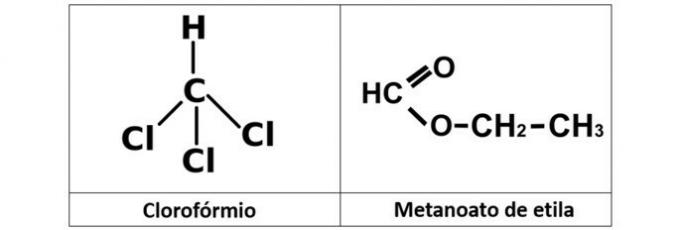
a) chloroform and ethyl methaneate
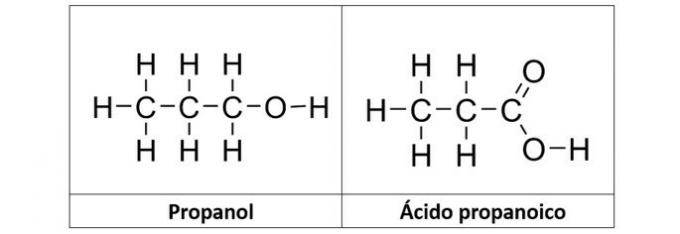
b) propanol and propanoic acid
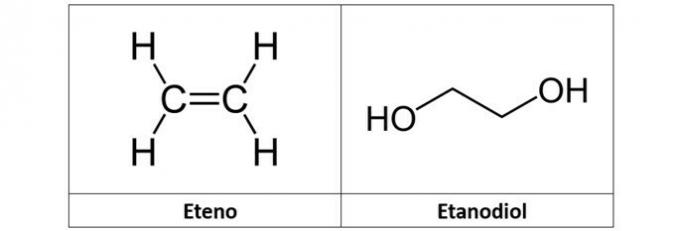
c) ethylene and ethanediol
d) ethanamide and benzene
Correct answer: b) propanol and propanoic acid
a) WRONG. We have chloroform (CHCl3), which is an alkyl halide, and the ethyl methanoate ester (C3H6O2), which contains oxygen in its structure.
b) CORRECT. In this alternative we have two compounds that have oxygenated organic functions. The propanol (C3H8O) is an alcohol formed by three carbons. The propanoic acid (C3H6O2) is a carboxylic acid.
c) WRONG. The ethylene (C2H4), also called ethylene, is an alkene-type hydrocarbon. Already ethanediol (C2H6O2) is an alcohol with two hydroxyls in its structure.
d) WRONG. Ethanamide (C2H5NO) is an amide and benzene is an aromatic hydrocarbon and, therefore, is formed only by carbon and hydrogen.

question 3
Look at the structure of the organic compound below and check the true statements.

(01) The compound has an organic nitrogen function.
(02) It is a primary amine, as it is linked to only one hydrogen.
(03) The name of the compound is diethylamine.
Right answer:
(01) CORRECT. The organic nitrogen function present in the compound is amine.
(02) WRONG. It is a secondary amine, as nitrogen is linked to two carbon chains.
(03) WRONG. The compound's name is dimethylamine, as there are two methyl radicals attached to nitrogen.
question 4
Eugenol, a member of the phenylpropanoid family, is an aromatic organic compound present in cloves, a spice used since ancient times.

Observe the structural formula of the compound and identify the organic functions present.
a) Alcohol and ether
b) Phenol and ether
c) Alcohol and ester
d) Phenol and ester
e) Alcohol and hydrocarbon
Correct alternative: b) Phenol and ether.
Eugenol has oxygenated organic functions in its chain, that is, in addition to carbon and hydrogen atoms, oxygen is a heteroatom present.
The phenol organic function is characterized by the hydroxyl (-OH) attached to an aromatic ring. In the ether function, oxygen is located between two carbon chains.
question 5
EDTA, whose full name is ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, is an organic compound with many applications. Its ability to bind metal ions makes it a chelating agent widely used both in the laboratory and industrially.
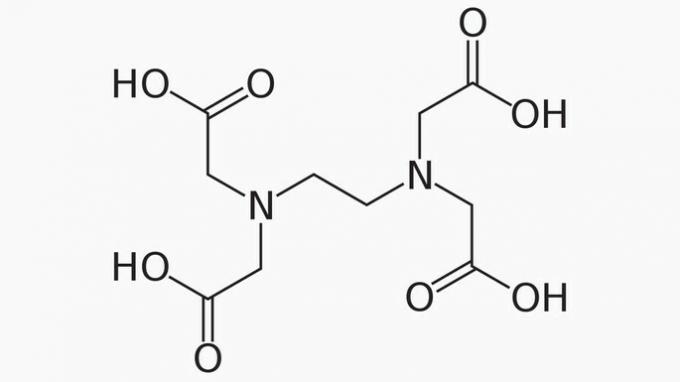
About EDTA, it is correct to state that the carbon chain is:
a) Open, homogeneous and unsaturated.
b) Closed, heterogeneous and saturated.
c) Open, heterogeneous and unsaturated.
d) Closed, homogeneous and saturated.
e) Open, heterogeneous and saturated.
Correct answer: e) Open, heterogeneous and saturated.
The EDTA chain is classified into:
OPEN. According to the arrangement of the carbon atoms in the structure of EDTA, we noticed that, due to the presence of ends, the chain of the compound is opened.
HETEROGENEOUS. In addition to carbon and hydrogen compounds, the carbon chain has nitrogen and oxygen heteroatoms.
SATURATED. The bonds between the carbon atoms are saturated, as the chain has only single bonds.
Learn more at: Organic chemistry.
entrance exam questions
question 1
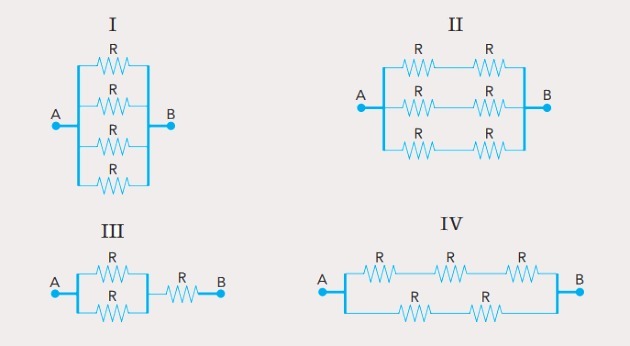
(UFSC) Observe the incomplete organic structures and identify the correct item(s):
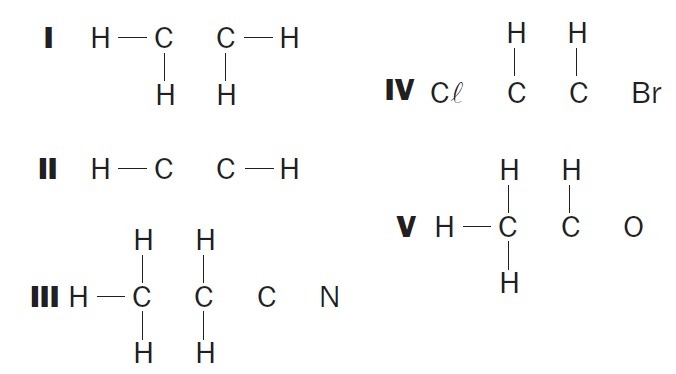
(01) Structure I lacks a single bond between the carbon atoms.
(02) Structure II lacks a triple bond between the carbon atoms.
(03) Structure III lacks two single bonds between carbon atoms and a triple between carbon and nitrogen atoms.
(04) Structure IV lacks two single bonds between carbon atoms and halogens and a double bond between carbon atoms.
(05) Structure V lacks a single bond between carbon atoms and a single bond between carbon and oxygen atoms.
Correct alternatives: 02, 03 and 04.
In addition to carbon, an obligatory chemical element in organic compounds, other elements may be present in structures and bonded by covalent bonds, where electrons are shared.
The valence of the elements determines the number of bonds that can be formed, as shown in the table below.
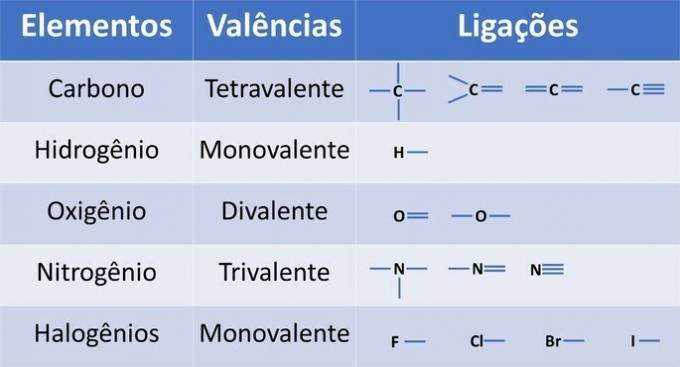
From this information, we have:
(01) WRONG. The structure lacks a double bond between the carbon atoms to form the ethene compound.
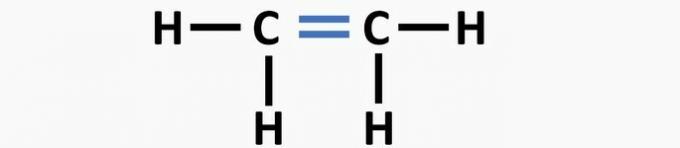
(02) CORRECT. The structure lacks a triple bond between the carbon atoms to form the ethyne compound.
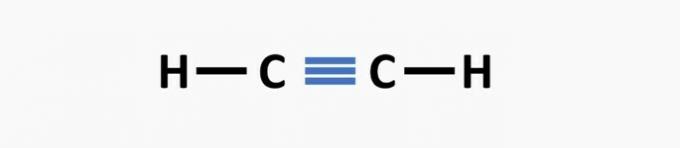
(03) CORRECT. The structure lacks single bonds between carbons, and triple bonds between carbon and nitrogen to form the compound propanenitrile.
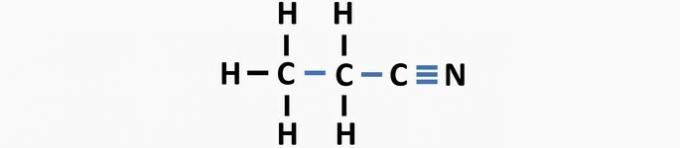
(04) CORRECT. The structure lacks single bonds between carbon and halogen, and double bonds between carbons to form the dichloroethene compound.
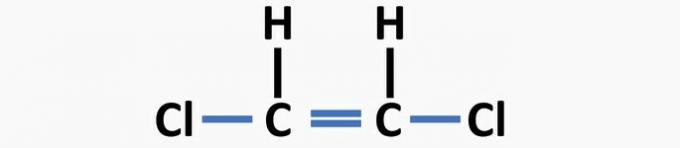
(05) WRONG. The structure lacks a single bond between carbons, and a double bond between carbon and oxygen to form the ethanal compound.
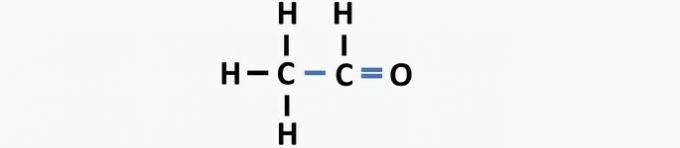
question 2
(UFPB) The structure of the organic compound of molecular formula C5H8What presents a branched, unsaturated, heterogeneous and alicyclic chain is:

Correct alternative: d.
Carbon chains can be classified as follows:
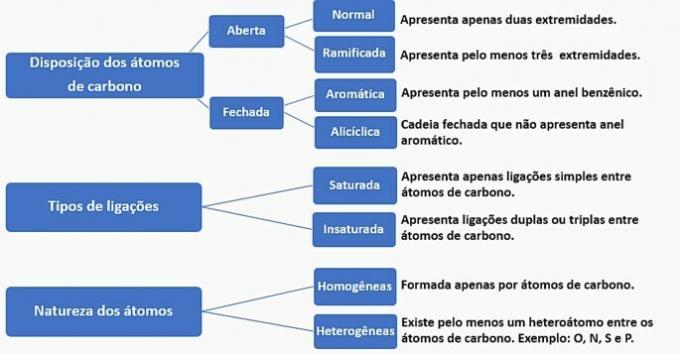
According to this information, we have:
a) WRONG. The chain is classified as normal, saturated, homogeneous and alicyclic.
b) WRONG. The chain is classified as normal, unsaturated, homogeneous and open.
c) WRONG. The chain is classified as branched, unsaturated, homogeneous and open.
d) CORRECT. The chain is classified as branched, unsaturated, heterogeneous and alicyclic, as
- It has a branch: methyl radical;
- Has unsaturation: double bond between carbons;
- It has a heteroatom: oxygen bonded to two carbons;
- It presents a closed chain: carbons linked in a circle without the presence of an aromatic ring.
e) WRONG. The chain is classified as branched, unsaturated, heterogeneous and open.
question 3
(Centec-BA) In the structure shown below, the numbered carbons are, respectively:
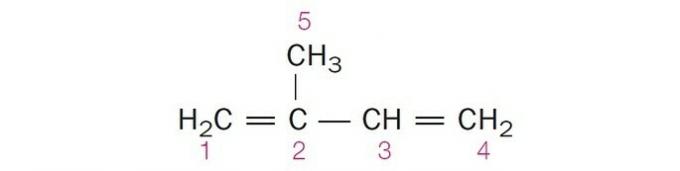
a) sp2, sp, sp2, sp2, sp3.
b) sp, sp3, sp2, sp, sp4.
c) sp2, sp2, sp2, sp2, sp3.
d) sp2, sp, sp, sp2, sp3.
e) sp3, sp, sp2, sp3, sp4.
Correct alternative: c) sp2, sp2, sp2, sp2, sp3.
Because it has 4 electrons in the valence shell, carbon is tetravalent, that is, it has a tendency to form 4 covalent bonds. These bonds can be single, double or triple.
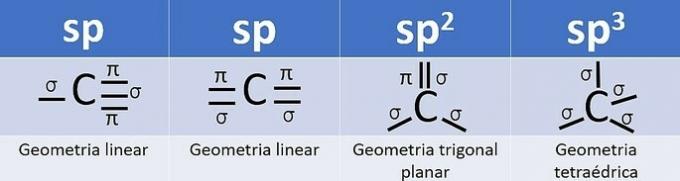
The number of hybrid orbitals is the sum of the sigma bonds (σ) of the carbon, since the bond does not hybridize.
- sp: 2 sigma links
- sp2: 3 sigma links
- sp3: 4 sigma links
According to this information, we have:
a) WRONG. Carbon 2 has sp hybridization2, as it has 3 σ bonds and one bond .
b) WRONG. Carbon has no sp hybridization4 and sp hybridization occurs when there is a triple bond or two double bonds between carbons.
c) CORRECT. The sum of the σ bonds on each carbon gives the alternative hybridization.
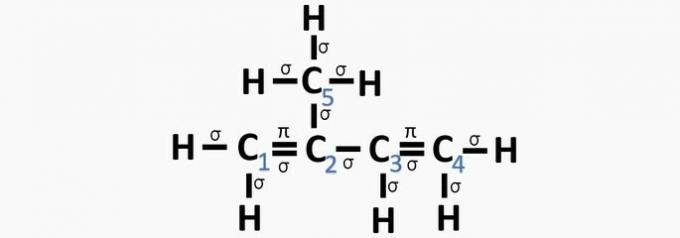
d) WRONG. Sp hybridization occurs when there is a triple bond or two double bonds between carbons.
e) WRONG. Carbon has no sp hybridization4 and sp hybridization occurs when there is a triple bond or two double bonds between carbons.
question 4
(UFF) There is a gaseous sample formed by one of the following compounds: CH4; Ç2H4; Ç2H6; Ç3H6 or C3H8. If 22 g of this sample occupy a volume of 24.6 L at a pressure of 0.5 atm and a temperature of 27 °C (Given: R = 0.082 L .atm. K–1.mol–1), it is concluded that it is the gas:
a) ethane.
b) methane.
c) propane.
d) propene.
e) ethene.
Correct alternative: c) propane.
1st step: convert the temperature unit from Celsius to Kelvin.
2nd step: calculate the number of moles of the compound using the general gas equation.
3rd step: calculate the molar mass of the compound.
4th step: find the hydrocarbon that has a molar mass of 44 g/mol.
Methane
Ethene
Ethane
propylene
Propane
Thus, it is concluded that the gas that corresponds to the information in the statement is propane.
question 5
(ITA) Consider the following substances:
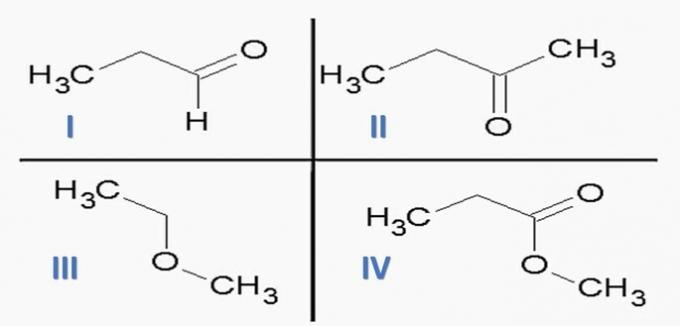
and the following chemical functions:
The. carboxylic acid;
B. alcohol;
ç. aldehyde;
d. ketone;
and. ester;
f. ether.
The option that CORRECTLY associates substances with chemical functions is:
a) Id; IIc; IIIe; IVf.
b) Ic; IId; IIIe; VAT
c) Ic; IId; IIIf; IVe.
d) Id; IIc; IIIf; IVe.
e) Ia; IIc; IIIe; IVd.
Correct alternative: c) Ic; IId; IIIf; IVe.
Organic functions are determined by structures and group organic compounds with similar characteristics.
The chemical functions present in the alternatives are:
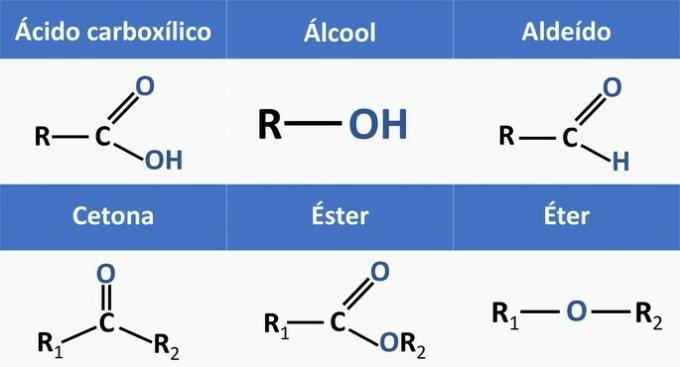
Analyzing the above structures and the compounds present in the statement, we have:
a) WRONG. The organ functions are correct, but the sequence is wrong.
b) WRONG. There is no carboxylic acid among the compounds.
c) CORRECT. Functional groups present in the compounds represent the following chemical functions.

d) WRONG. I is aldehyde and II is ketone.
e) WRONG. There is no carboxylic acid among the compounds.
Learn more at: Organic Functions.
Enem questions
question 1
(Enem/2014) One method for determining the ethanol content in gasoline consists of mixing known volumes of water and gasoline in a specific bottle. After shaking the flask and waiting for a period of time, the volumes of the two immiscible phases that are obtained are measured: one organic and the other aqueous. Ethanol, once miscible with gasoline, is now miscible with water.
To explain the behavior of ethanol before and after the addition of water, it is necessary to know
a) the density of liquids.
b) the size of the molecules.
c) the boiling point of liquids.
d) the atoms present in the molecules.
e) the type of interaction between the molecules.
Correct alternative: e) the type of interaction between the molecules.
Intermolecular forces influence the solubility of organic compounds. Substances tend to dissolve with each other when they have the same intermolecular force.
See in the table below some examples of organic functions and the type of interaction between molecules.
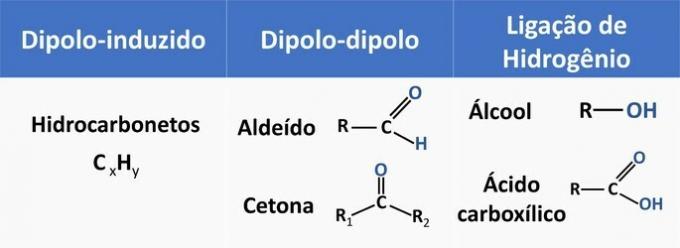
Ethanol is considered a polar solvent, as it has a polar group (—OH) in its structure. However, its carbon chain, being non-polar (CH) is capable of interacting with non-polar solvents. Therefore, ethanol solubilizes both in water and in gasoline.
According to this information, we have:
a) WRONG. Density relates the mass of a body to the occupied volume.
b) WRONG. The size of the molecules influences the polarity of the compounds: the larger the carbon chain, the more nonpolar the substance becomes.
c) WRONG. The boiling point is useful for separating molecules: distillation separates compounds with different boiling points. The lower the boiling point, the more easily the molecule is vaporized.
d) WRONG. An aldehyde has carbon, hydrogen and oxygen in its structure. This compound performs dipole-dipole interactions, while an alcohol, having the same elements, is capable of forming hydrogen bonds.
e) CORRECT. The interaction of ethanol with water (hydrogen bonding) is more intense than with gasoline (diplo-induced).
question 2
(Enem/2013) The molecules of nanoputians they resemble human figures and were created to stimulate the interest of young people in understanding the language expressed in structural formulas, widely used in organic chemistry. An example is NanoKid, represented in the figure:
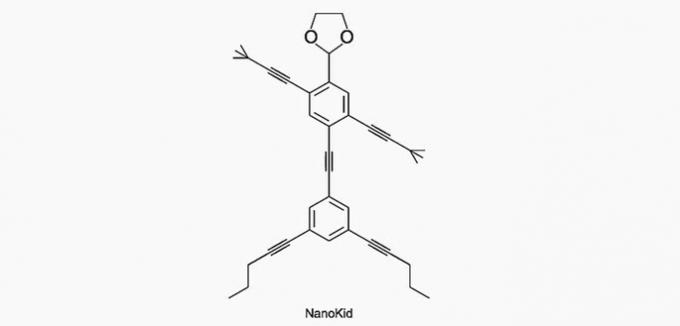
Where in the NanoKid's body is there quaternary carbon?
a) Hands.
b) Head.
c) Chest.
d) Abdomen.
e) Feet.
Correct alternative: a) Hands.
Carbon is classified as follows:
- Primary: binds to a carbon;
- Secondary: binds to two carbons;
- Tertiary: binds to three carbons;
- Quaternary: binds to four carbons.
See the examples below.

According to this information, we have:
a) CORRECT. The carbon in the hand is bonded to four other carbons, so it's quaternary.
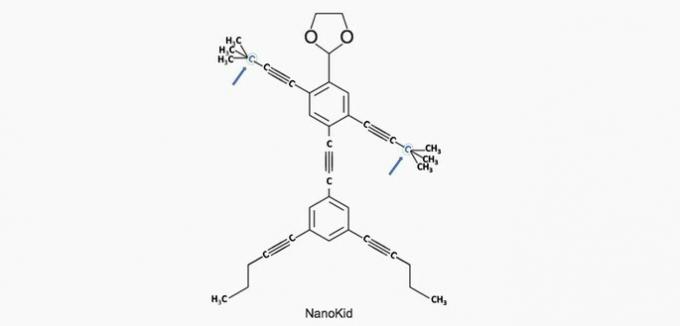
b) WRONG. The head is made up of primary carbons.
c) WRONG. The chest is made up of secondary and tertiary carbons.
d) WRONG. The abdomen is made up of secondary carbons.
e) WRONG. The feet are made of primary carbons.
question 3
(Enem/2014) Some polymeric materials cannot be used for the production of certain types of artifacts, either for limitations of mechanical properties, either by the ease with which they suffer degradation, generating undesirable by-products for that application. Therefore, inspection becomes important to determine the nature of the polymer used in the manufacture of the artifact. One of the possible methods is based on the decomposition of the polymer to generate the monomers that gave rise to it.
Controlled decomposition of an artifact generated diamine H2N(CH2)6NH2 and the HO diacid2C(CH2)4CO2H. Therefore, the artifact was made of
a) polyester.
b) polyamide.
c) polyethylene.
d) polyacrylate.
e) polypropylene.
Correct alternative: b) polyamide.
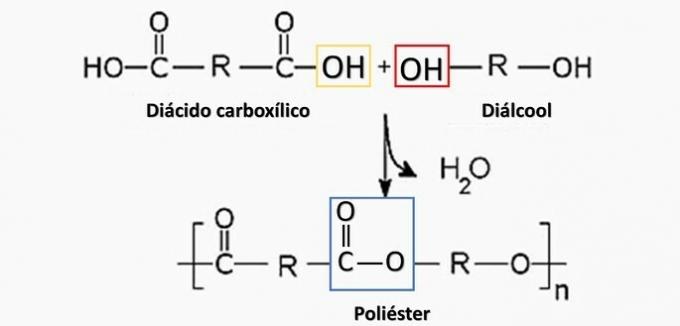
a) WRONG. Polyester is formed in the reaction between a dicarboxylic acid (—COOH) and a dialcohol (—OH).
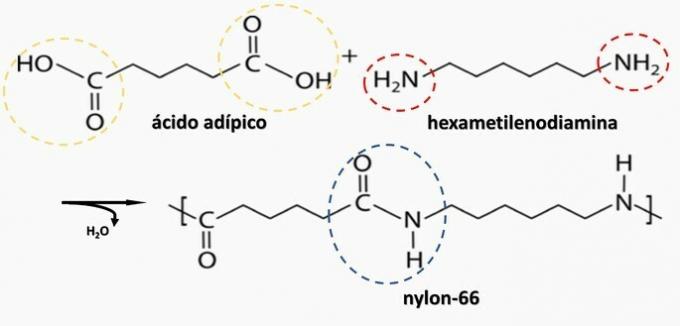
b) CORRECT. Polyamide is formed by the polymerization of a dicarboxylic acid (—COOH) with a diamine (—NH2).
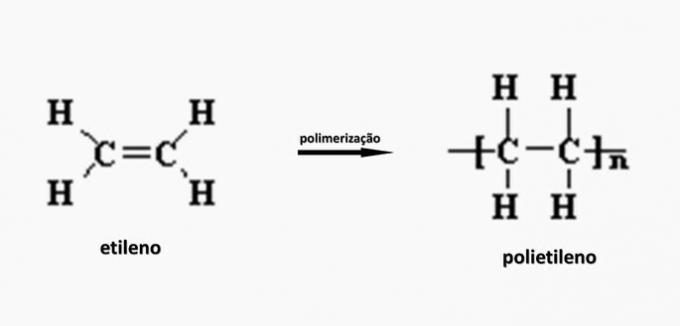
c) WRONG. Polyethylene is formed in the polymerization of ethylene monomer.
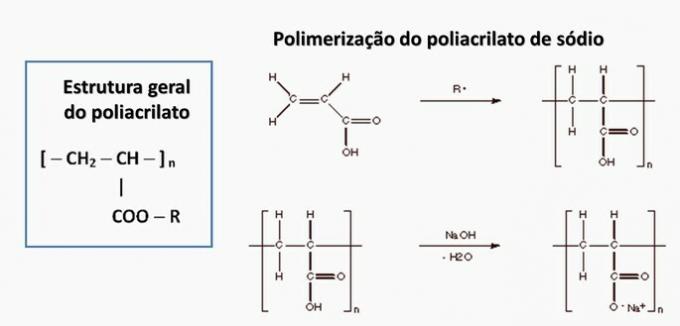
d) WRONG. Polyacrylate is formed by a salt derived from carboxylic acid.
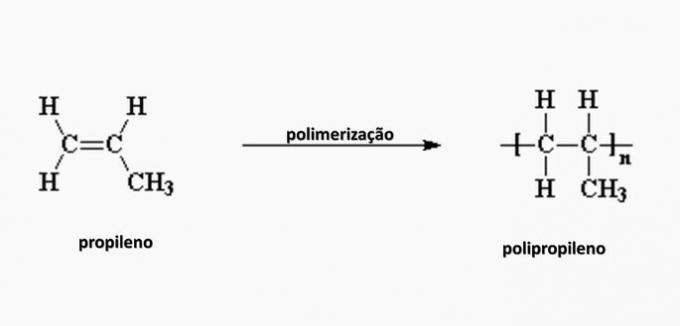
e) WRONG. Polypropylene is formed in the polymerization of propylene monomer.
question 4
(Enem/2008) China has committed to indemnify Russia for the spillage of benzene from an industry Chinese petrochemicals in the Songhua River, a tributary of the Amur River, which forms part of the border between the two countries. The president of the Federal Water Resources Agency of Russia assured that the benzene will not reach the pipelines of drinking water, but asked the population to boil running water and avoid fishing in the Amur river and its tributaries. Local authorities are storing hundreds of tons of coal, as the mineral is considered an effective benzene absorber. Internet: (with adaptations). Taking into account the measures adopted to minimize damage to the environment and the population, it is correct to state that
a) coal, when placed in water, reacts with benzene, eliminating it.
b) benzene is more volatile than water and, therefore, it needs to be boiled.
c) the orientation to avoid fishing is due to the need to preserve fish.
d) benzene would not contaminate drinking water pipes, as it would be naturally decanted at the bottom of the river.
e) the pollution caused by the Chinese industry's benzene spill would be restricted to the Songhua River.
Correct alternative: b) benzene is more volatile than water and therefore it is necessary that it be boiled.
a) WRONG. Coal contains in its structure several pores and is used as an adsorbent, as it is capable of interacting with contaminants and retaining them on its surface, but not eliminating them.
b) CORRECT. The greater the volatility of a substance, the more easily it changes into a gaseous state. While the boiling point of water is 100°C, that of benzene is 80.1°C. This is because water is a polar compound and benzene is a non-polar compound.
The type of interactions molecules make are different and also affect the boiling point of substances. The water molecule is capable of making hydrogen bonds, a type of interaction much stronger than that which benzene, with the induced dipole, is able to make.
c) WRONG. In a food chain, one being becomes another's food according to the interactions of species in a location. When a toxic substance is released into an environment, there is progressive accumulation and fish contaminated, when ingested by man, can take benzene with them and cause DNA mutations and even even cancer.
d) WRONG. Benzene has a lower density than water. Thus, the trend is that even underwater it continues to spread.
e) WRONG. Seasonal changes can further increase the problem, as low temperatures decrease the biological decomposition capacity of chemicals by the action of the sun or bacteria.
question 5
(Enem/2019) Hydrocarbons are organic molecules with a series of industrial applications. For example, they are present in large amounts in the various petroleum fractions and are usually separated by fractional distillation based on their boiling temperature. The table shows the main fractions obtained from the distillation of oil at different temperature ranges.
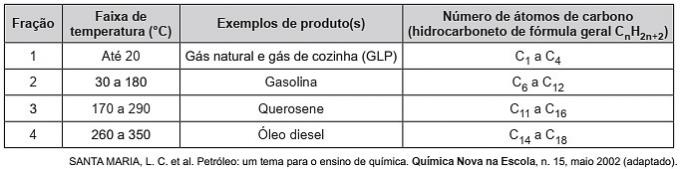
In fraction 4, the separation of compounds occurs at higher temperatures because
a) their densities are greater.
b) the number of branches is greater.
c) its solubility in oil is greater.
d) intermolecular forces are more intense.
e) the carbon chain is more difficult to break.
Correct alternative: d) the intermolecular forces are more intense.
Hydrocarbons interact by induced dipole and this type of intermolecular force is intensified with the increase of the carbon chain.
Therefore, the heavier petroleum fractions have a higher boiling temperature, as the chains interact more strongly by an induced dipole.
For more exercises, with commented resolution, see also:
- Exercises on Hydrocarbons
- Exercises on Organic Functions
- Chemistry Questions in Enem